
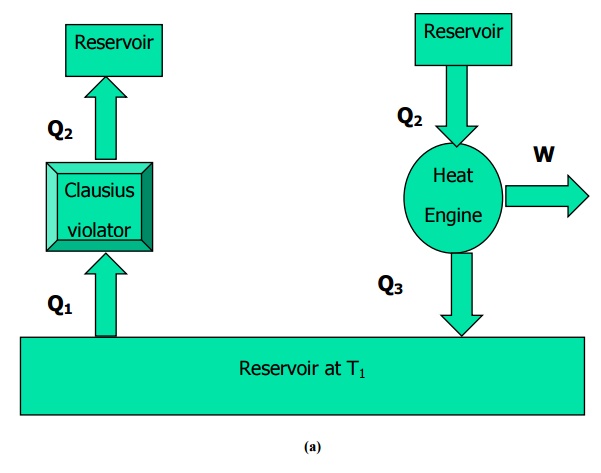
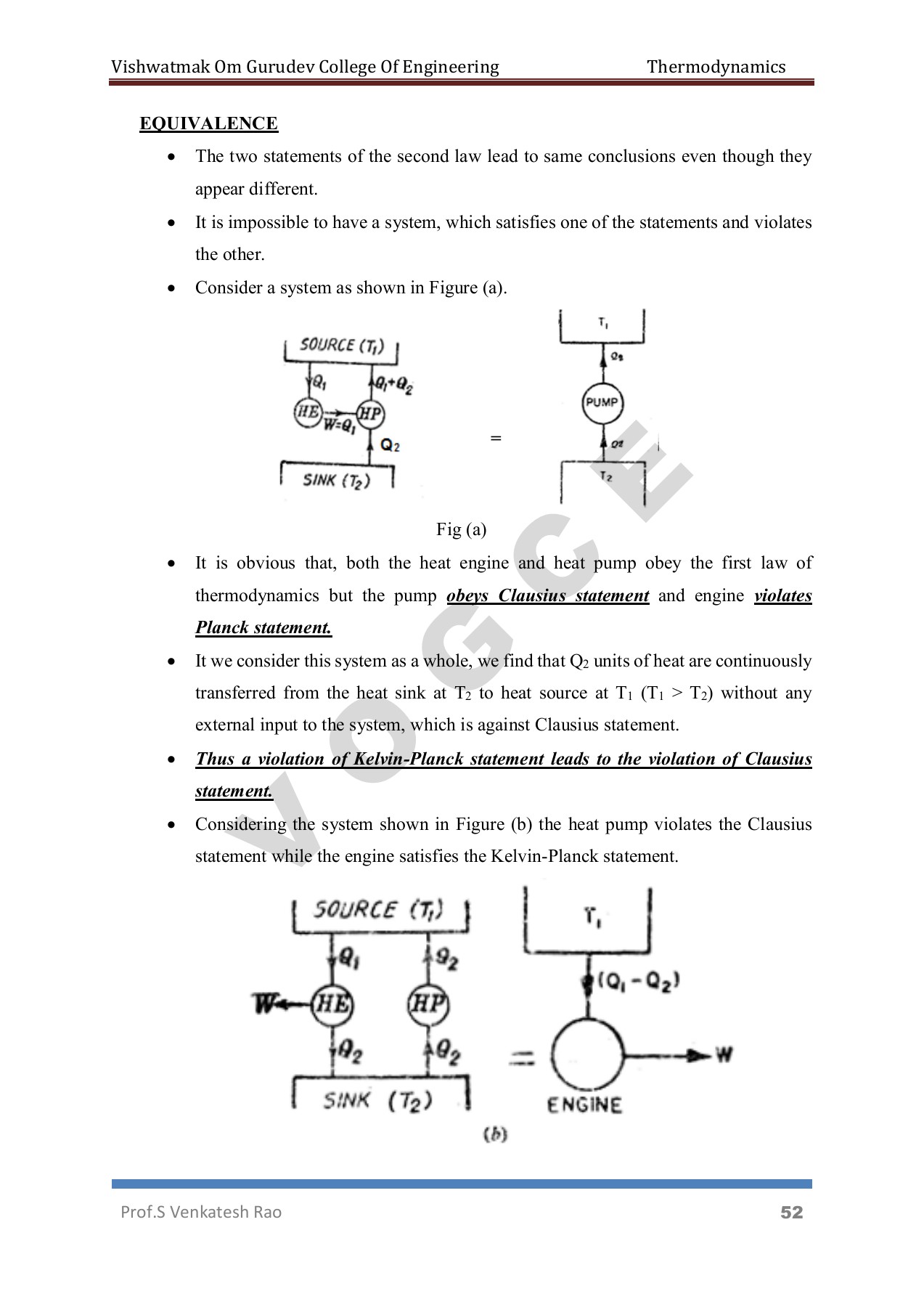
The second law of Thermodynamics is an empirical law that is not deduced from any previous law. It states that as energy is transferred or transformed, more and more of it is wasted. The Second Law of Thermodynamics is about the quality of energy. Heat can never pass from a colder to a warmer body without some other change, connected therewith, occurring at the same time. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed the total quantity of energy in the universe stays the same. For example, we cannot construct a refrigerator that operates without any work input. That is, heat transfer can only occur spontaneously in the direction of temperature decrease. This statement is related to refrigerators and heat pumps. Clausius Statement from the second law of thermodynamics states that: It is impossible to design a device which works on a cycle and produce no other effect other than heat transfer from a cold body to a hot body.
In addition to the Kelvin-Planck statement, the the Clausius statement also describes the 2nd law.
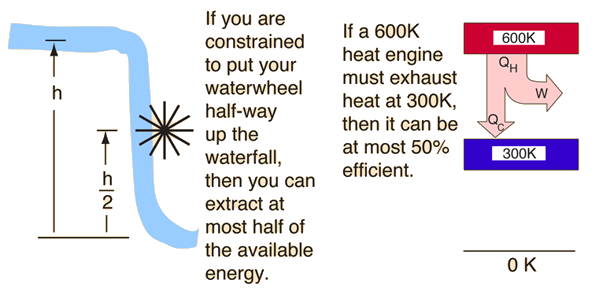
This statements is related to heat engines. Clausius states that it is impossible for a self-acting machine, unaided by any external agency, to transfer heat from a body at a lower temperature to. One of these statements is called the Kelvin-Planck statement. This fact is known as the Clausius statement of the second law of Thermodynamics: The 2nd law of thermodynamics can be described by two classical statements. The purpose of a heat pump is to transfer the largest possible amount of heat from the cold to the hot thermal reservoir for a given amount of work input there is however a limit to the amount of heat that can be transferred. The internal energy variation per cycle of the working fluid is zero (because the internal energy is a state function), therefore: In addition, as energy is conserved, theheat pump must satisfy the first law of Thermodynamics. The coefficient of performance (COP) of the heat pump is the ratio of heat absorbed from the cold thermal reservoir to the absolute value of work required: Or Heat can not itself flow from colder body to a hotter body. The operation of a heat pump requires work to be done by an external energy source.ĭepending on the design of heat pump, the processes undergone by the working fluid will be different, but they will always consist of a anticlockwise cycle, because work (negative) will have to be done by the surroundings (W<0): Clausius’s statement: It is impossible to construct a device (operating in a cycle) that can transfer heat from cold body to the hot body without absorbing any work. A thermal reservoir is a thermodynamic system that can transfer heat indefinitely at constant temperature.
During the cycle, the working fluid absorbs heat from the cold thermal reservoir at temperature T 2 (in blue in the figure), and transfers it to a warmer thermal reservoir at temperature T 1 (in yellow).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
